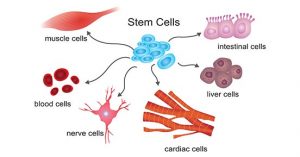
Cellular differentiation determines cell fate
Cell differentiation Recombinants is the process in which a cell changes from one type to many different types. In the process of cell differentiation, there are differences in morphological structure and physiological function. All organisms start from a single cell. For example, humans derive from fertilized eggs, and this process involves the differentiation of embryonic stem cells. Cellular differentiation occurs throughout life. For example, hematopoietic stem cells differentiate into various immune cells. The abnormal differentiation of cells can lead to cancer cells. Cancer cells divide indefinitely, forming tumours and endangering human health.
Cellular differentiation involves a variety of signal transduction processes:
1. MAPK signalling pathway
2. Phosphatidylinositol (PLC) signalling pathway
3. cAMP/PKA signalling pathway
4. Via JAK-STAT
5. PI3K-AKT-mTOR signalling pathway
6. Wnt signalling pathway
7. TGF-β Superfamily Signaling Pathway
1. MAPK signalling pathway
MAPK is a mitogen-activated protein kinase, a class of protein kinases with dual phosphorylation of serine and tyrosine in the cytosol. The MAPK signalling pathway activates transcription factors and regulates gene expression through a cascade reaction (MAPKKK-MAPKK-MAPK). MAPK can trigger the activation of transcription factors in the nucleus, participate in the process of signalling from the cell surface to the nucleus, and regulate cell proliferation and differentiation. Currently, there are 4 known MAPK signalling pathways, including the extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK, also known as SAPK), p38, and ERK5 pathways.
1.1 ERK-MAPK signalling pathway
In the MAPK signalling pathway, the ERK pathway acts mainly through the Ras-Raf-MEK-ERK cascade. The main process of this pathway: the growth factor activates the receptor by binding to the receptor tyrosine kinase, and the activated receptor tyrosine kinase activates the Ras protein, then the Ras protein phosphorylates Raf, and the activated Raf phosphorylates the MEK waters. below. MEK can phosphorylate and activate ERK, which is transferred to the nucleus and regulates gene expression by activating other kinases or transcription factors.
The ERK-MAPK signalling pathway plays a role in the differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) into adipocytes. In the early stage of adipocyte differentiation, ERK1/2 promotes adipocyte differentiation by promoting the expression of C/EBPα and PPARγ. In the late stage of adipocyte differentiation, activated ERK1/2 phosphorylates PPARγ to inactivate it and inhibit adipocyte differentiation. This pathway can also affect the proliferation and differentiation of red blood cells. Studies have shown that the ERK signalling pathway is also involved in signal transduction of osteoblast differentiation and proliferation.
1.2 Via JNK-SAPK
c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), also known as stress-activated protein kinase (SAPK), is another subclass of MAPK in mammals. The JNK signalling pathway can affect a variety of vital processes, such as cell growth, cell differentiation, and cell death. JNK can change the level of osteocalcin mRNA, thus JNK activation can induce osteoblast differentiation. The JNK signalling pathway also plays an important role in the regulation of adipocyte differentiation.
1.3 via p38 MAPK
The p38 signalling pathway is an important component of the MAPK family. p38 MAPK can be activated by a variety of extracellular stress responses, including ultraviolet rays, radiation, and proinflammatory factors. The p38 pathway plays a very important role in the osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). Inhibition of the p38 MARK pathway downregulates the activity of protein kinase C (PKC), which plays an important role in the osteogenic differentiation of cells.
In addition, the transforming growth factor and the bone morphogenetic protein BMP-2 induce the transcriptional expression of Runx2/Cbfa1 through the p38 MAPK pathway. Among them, Runx2 is a key target gene affecting osteogenic activity, and Cbfa1 regulates MSC differentiation into osteoblasts at the transcriptional level.
2. Phosphatidylinositol (PLC) signalling pathway
In the phosphatidylinositol signalling pathway, extracellular signalling molecules bind to G protein-coupled receptors, activating phospholipase C (PLC-β) on the plasma membrane, causing phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate ( PIP2) to be hydrolyzed to inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate (IP3) and diacylglycerol (DG). Therefore, the phosphatidylinositol (PLC) signalling pathway is also called the “dual messenger system”.
IP3 turns on the calcium channel and initiates signals downstream. Ca2+ binds to calmodulin (CaM) to form a Ca2+-CaM complex, which activates adenylate cyclase (AC) and phosphodiesterase (PDE); activates Ca2+-CaM dependent protein kinase. DAG activates PKC, phosphorylates serine/threonine residues of proteins, and produces different cellular responses, such as cell secretion, muscle contraction, cell proliferation and differentiation. The PLC-γ pathway is also involved in the differentiation of red blood cells.
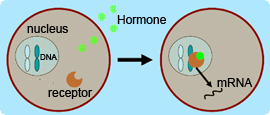
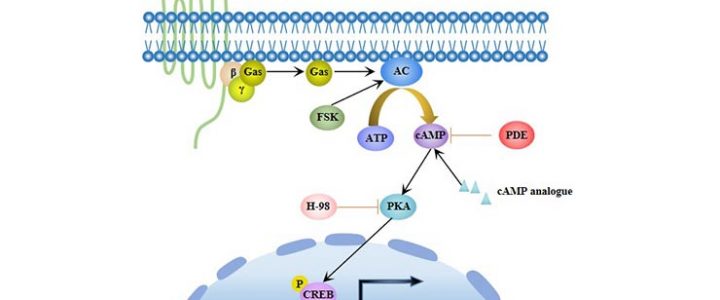
3. cAMP/PKA signalling pathway
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) is an important intracellular signalling molecule, activates cAMP-dependent protein kinase A (PKA), and regulates cell differentiation. cAMP/PKA signalling can promote the adipogenic differentiation of MSCs and inhibit their osteogenic differentiation.
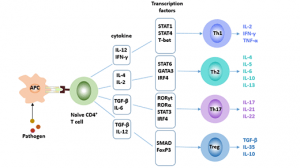
4. Via JAK-STAT
JAK is a tyrosine kinase whose main substrate is the STAT transcription factor. Activated STAT translocates to the nucleus and binds to the DNA sequence, thus regulating gene expression. The JAK-STAT pathway plays an important role in cell proliferation, apoptosis, and differentiation.
The main process of this signal pathway is as follows:
- The binding of the ligand to the receptor leads to receptor dimerization. Dimerized receptors activate JAK, JAK phosphorylation STAT. Phosphorylated STAT forms dimers that enter the nucleus and bind to DNA sequences to regulate gene expression.
- The JAK/STAT pathway plays an important role in the proliferation and differentiation of red blood cells.
5. PI3K-AKT-mTOR signalling pathway
The mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) is a conserved serine/threonine-protein kinase with two main forms: mTORC1 and mTORC2. Activated mTOR plays a key regulatory role in cell proliferation, differentiation, and metabolism. mTOR is primarily regulated by the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signalling pathway and the LKB1/AMPK/mTOR signalling pathway.
These two signalling pathways are the main pathways that regulate the proliferation and differentiation of testicular support cells. In the mTOR signalling pathway, deletion of the mTOR gene leads to a decrease in the number of testicular support cells. Studies have shown that PI3K-activated Akt kinase plays an important role in hematopoiesis. The PI3K pathway is also important in small intestinal stem cell regeneration and in promoting cell differentiation.
6. Wnt signalling pathway
The Wnt signalling pathway is highly conserved and the central component of this signalling pathway is β-catenin. When the Wnt signal is not activated, intracellular β-catenin is phosphorylated and degraded by the proteasome. When the Wnt protein binds to its receptor Frizzled and LRP, the β-catenin degradation complex is inactivated, β-catenin is released and accumulates in the cell. Accumulated β-catenin enters the nucleus and binds to transcription factor and T-cell factor/lymphocyte-enhancing factor (TCF/LEF) to initiate a series of proliferation-related genes.
6.1 Wnt signalling pathway and adipocyte differentiation
Activation of the Wnt signalling pathway can inhibit fat cell differentiation, and once this pathway is out of control, obesity can occur. The Wnt signalling pathway is activated by interleukin-6 (IL-6) and tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), which inhibits β-catenin degradation. β-catenin further inhibits downstream levels of C/EBP and PPAR, impairing or even preventing adipocyte differentiation.
Fat cell differentiation was also affected by the PPAR signalling pathway and the Hedgehog signalling pathway. The PPAR family plays an important role in fat differentiation and metabolism. Among them, PPARγ, as an important transcription factor for adipogenic differentiation, can accelerate adipocyte differentiation and deposition.
6.2 Wnt signalling pathway and cartilage differentiation
Activation of the Wnt signalling pathway can promote chondrocyte differentiation. During chondrogenic differentiation, the Wnt signalling pathway acts in conjunction with many other pathways. In cartilage differentiation, TGF-β and Wnt signalling pathways together promote cartilage differentiation from mesenchymal stem cells. In addition, the Wnt signalling pathway can promote small intestinal stem cell differentiation and cardiomyocyte differentiation, and promote the proliferation and differentiation of testicular support cells.
7. TGF-β Superfamily Signaling Pathway
The TGF-β superfamily regulates cell growth, proliferation, differentiation, migration, and apoptosis, regulates embryonic development, participates in the body’s immune response, and has multifunctional biological activities. The TGF-β signalling pathway affects the proliferation and differentiation of testicular support cells.






![[Prospects for molecular-genetic support of research on proteolytics in the necrobiome composition] [Prospects for molecular-genetic support of research on proteolytics in the necrobiome composition]](https://osumolgen.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/03/IMG-20201217-WA0091-720x300.jpg)
![[Prospects for molecular-genetic support of research on proteolytics in the necrobiome composition]](https://osumolgen.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/03/IMG-20201217-WA0091-300x142.jpg)